# HDR
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light traveling in a given direction. measured in candela per square meter (cd/m^2)
- Human static contrast ration:
:1 -> about 65 f-stops - Human dynamic contrast ration:
:1 -> about 20 f-stops
Challenge with expressing brightness effectively in images
- Need about 5-10 million values to store all brightness around
- 8-bit images provide only 256 values
- so you end up capturing values only in one side of the spectrum (focusing on either the dark side of the spectrum or bright side of the spectrum)
# Image Acquisition Pipeline
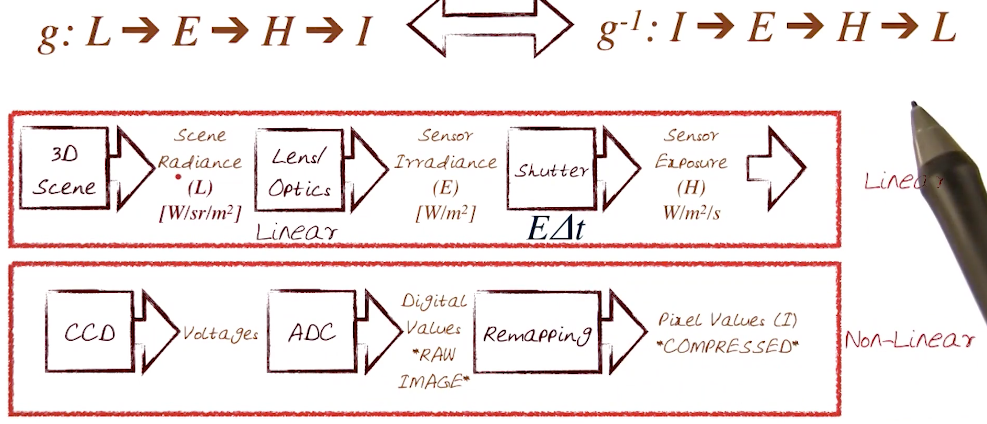
# Camera Calibration
Geometric: How pixel coordinates relate to directions in the world
Radiometric/Photometric: How pixel values relate to radiance amounts in the world
Panorama: How pixel coordinates relate to directions in other images
HDR: How pixel values relate to radiance amounts in other image
# Radiometric Calibration
- A color chart with known reflectances
- Multiple camera exposures to fill up the curve
- Method assumes constant lighting on all patches and works best when source is far away (example sunlight)
- Unique inverse exists because g is monotonic and smooth for all cameras
# Response Curves
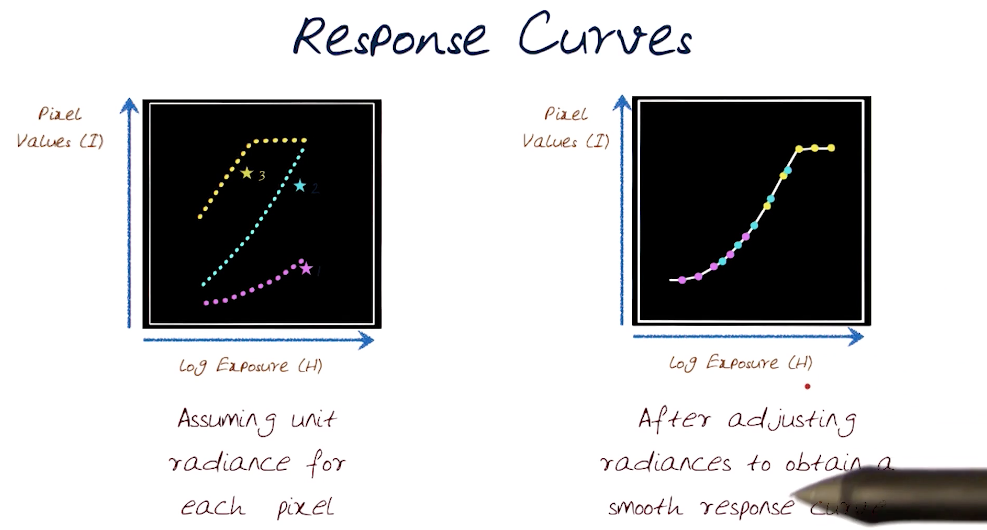
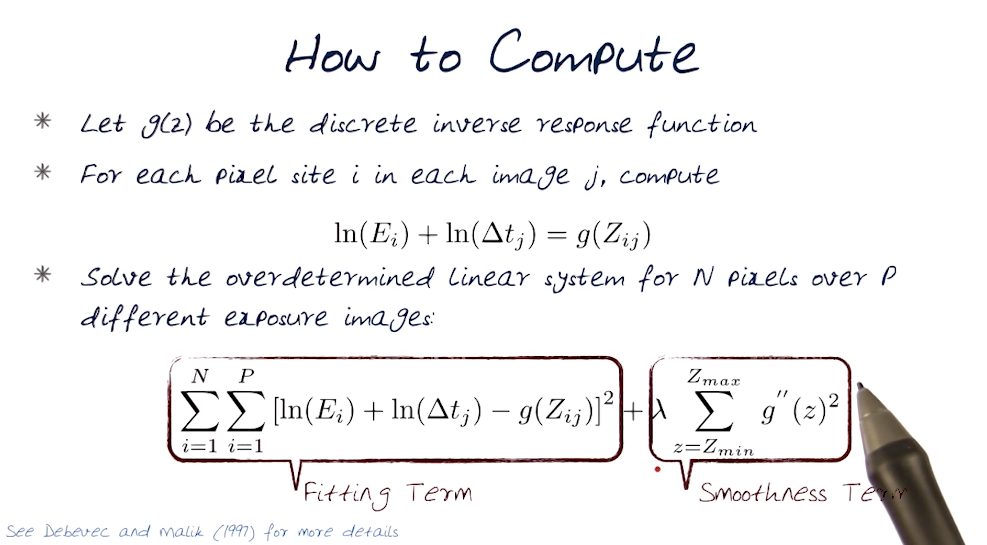
# Computing Response Curve
# Radiance map formats
Require an additional dimension to record expontent
# Tone Mapping
- Map one set of colors to another
- Displaying on a medium that has limited dynamic range
- printers, monitors and projectors all have a limited dynamic range
- Inadequate to reproduce the full range of light intensities present in natural scenes
- Addresses the problem of
- Strong contrast reduction from the scene radiance to the displayable range
- preserves the image details and color appearance
- many well-known algorithms exist for this
- See Banterle, et al. (2011), Reinhard et al. (2002) and Durang and Dursey (2002)
